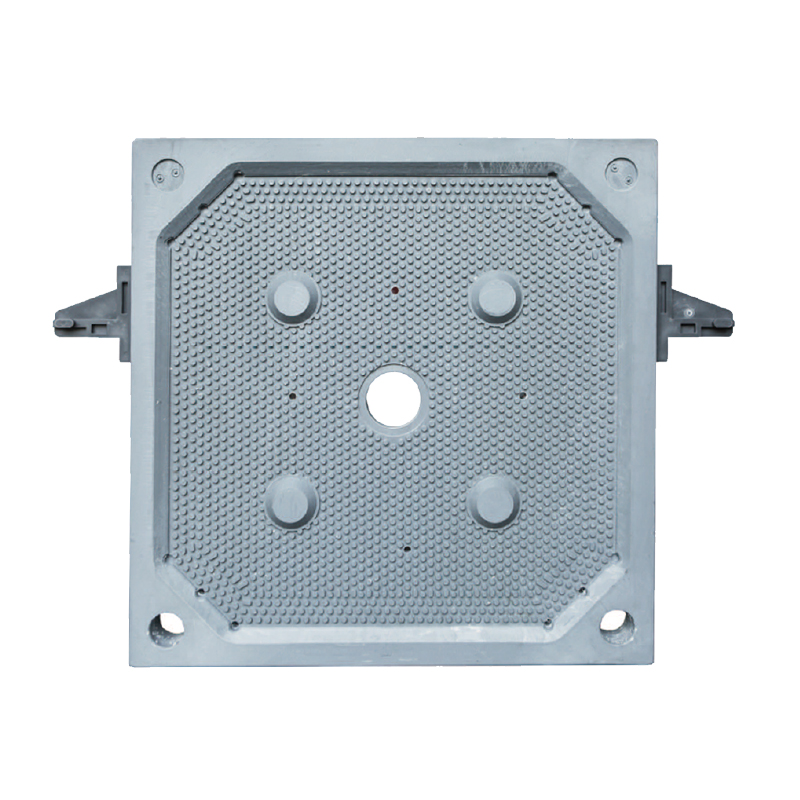
What’s the difference between a plate and frame filter press and a belt filter press? Which is right for your project?
 2025.11.03
2025.11.03
 Industry News
Industry News
In the field of industrial solid-liquid separation, Filter Press and Belt Filter Press are the two most commonly used types of filtration equipment. Although both are used to separate solids from slurry or suspension, they differ significantly in working principle, processing capacity, maintenance costs, and applicable scenarios. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the equipment best suited to your project needs.
1. Difference in Working Principle
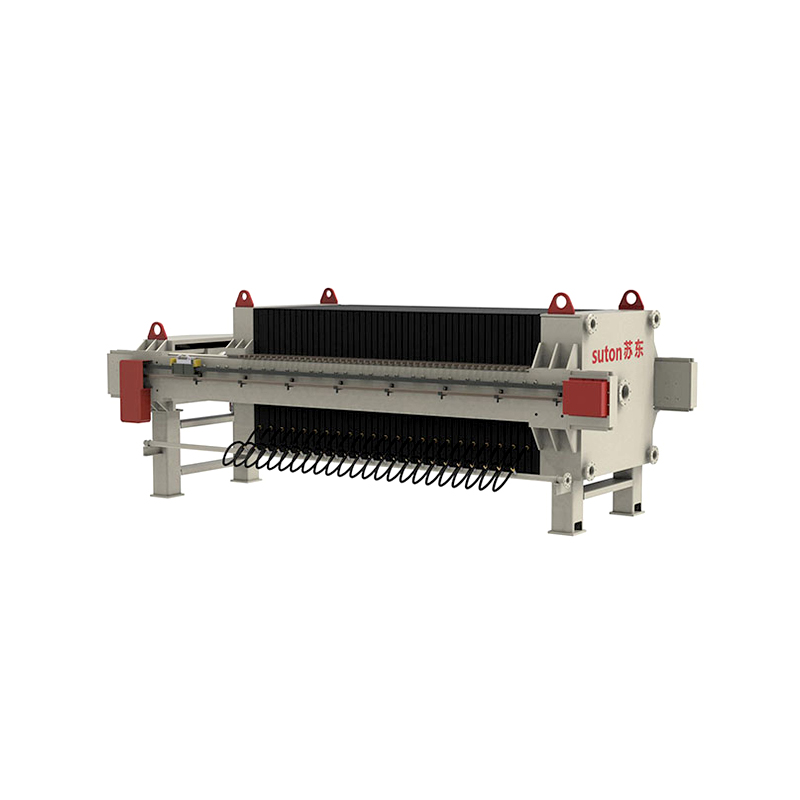
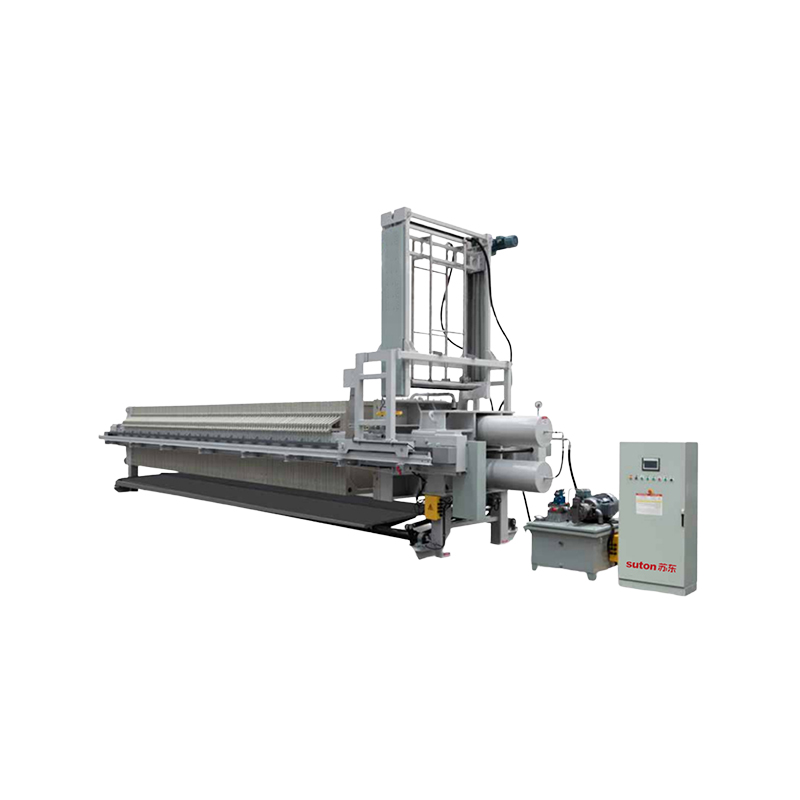
Filter Press
A filter press consists of multiple filter plates and frames arranged alternately to form chambers. Slurry is pumped into these chambers, where the filter cloth allows liquid to pass through while solids gradually accumulate to form a filter cake. The press applies high pressure during filtration, resulting in a low moisture content in the cake. Since a filter press operates in batch mode, the plates must be opened manually or automatically to remove the cake after each cycle. This design is ideal for handling high-concentration, coarse, or viscous slurries.
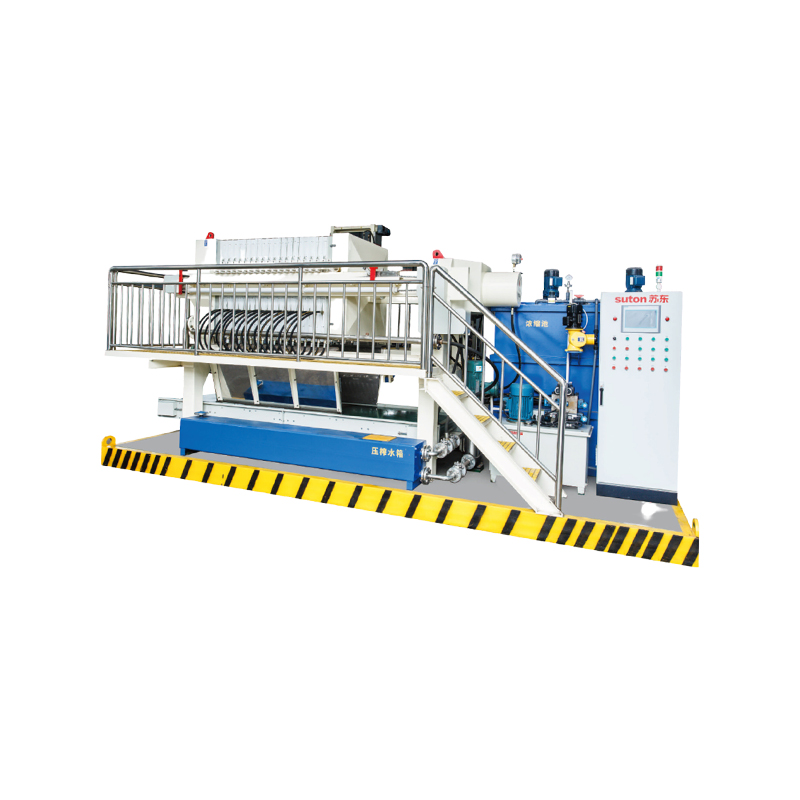
Belt Filter Press
A belt filter press uses one or more continuously moving filter belts to separate solids from suspension via gravity, vacuum suction, and mechanical squeezing. Slurry enters the feeding section and passes through a gravity drainage zone and a compression zone, forming a filter cake that is continuously discharged by the conveyor. Unlike a filter press, a belt filter press operates continuously, making it more suitable for low-concentration suspensions and large-scale continuous production.
2. Processing Capacity and Output
|
Feature |
Filter Press |
Belt Filter Press |
|
Slurry Concentration |
High (>5%-10%) |
Low (1%-5%) |
|
Operation Mode |
Batch operation (load → filter → unload) |
Continuous operation (slurry constantly enters, cake constantly discharged) |
|
Processing Capacity |
Suitable for medium to small projects |
Suitable for large-scale continuous production |
|
Filter Cake Moisture |
Low (dry) |
High (wet) |
Filter presses are limited by the number of chambers and pump capacity, making them suitable for medium or small projects. The dry cake facilitates transport and further recovery. Belt filter presses are suitable for handling large volumes of low-concentration slurry continuously, but the filter cake moisture is relatively high, requiring secondary drying if needed.
3. Maintenance and Cost
Filter Press advantages: strong capability for high-concentration slurry, dry filter cake for easy transport or recovery.
Disadvantages: complex structure, requires regular cleaning and replacement of filter cloth, and manual intervention during operation. Initial investment is high, but low moisture in the filter cake reduces subsequent processing costs.
Belt Filter Press advantages: simple operation, continuous production, long filter cloth life, minimal manual intervention, ideal for large-scale continuous production.
Disadvantages: high moisture in the filter cake increases transport or secondary processing costs; not suitable for high-concentration or coarse slurry.
Maintenance comparison: filter presses require more manual attention but produce dry cake; belt filter presses are easier to maintain but produce wetter cake.
4. Applicable Scenarios
Filter Press suitable scenarios:
- High-concentration slurries such as mining tailings, chemical precipitates, pharmaceutical wastewater.
- Situations requiring dry filter cake for transport, storage, or solid recovery.
- Batch production projects, medium processing volume, high filtration precision, and low moisture content.
Belt Filter Press suitable scenarios:
- Low-concentration suspensions such as municipal wastewater, paper mill wastewater, and food processing wastewater.
- Continuous high-volume production with automation.
- Filter cake moisture requirements are not strict, secondary processing possible.
5. Selection Recommendations
- For high-concentration slurry projects where dry cake is required, and processing volume is medium to small → choose Filter Press
- For low-concentration slurry projects, large-scale continuous production → choose Belt Filter Press
Selecting the right filtration equipment improves production efficiency and reduces operational costs. Filter presses are ideal for high-concentration slurry and dry cake needs, while belt filter presses suit low-concentration, high-volume continuous production.

 English
English Español
Español हिंदी
हिंदी Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt