Filter Press vs. Belt Filter: Which One Is Better for Your Filtration Needs?
 2025.10.06
2025.10.06
 Industry News
Industry News
Introduction
Filtration is a critical process in many industrial sectors, from wastewater treatment and chemical processing to mining and food production. Two commonly used filtration systems are Filter Presses and Belt Filters. Both of these technologies are used to separate solids from liquids, but they operate differently and are suited to different applications. Understanding the differences between them is key to choosing the right system for your needs.

What Is a Filter Press?
Definition and Functionality
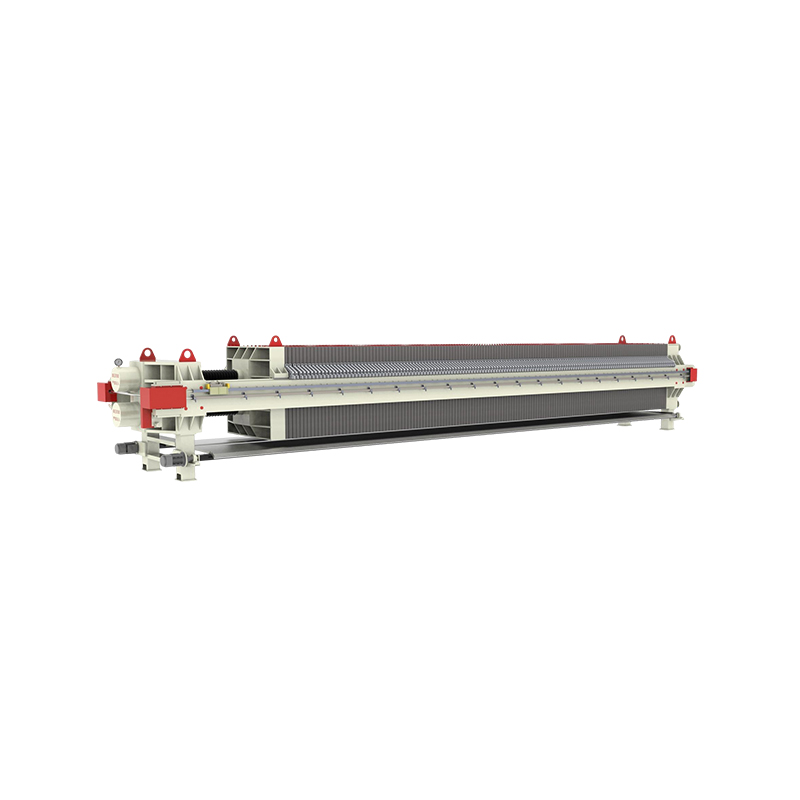
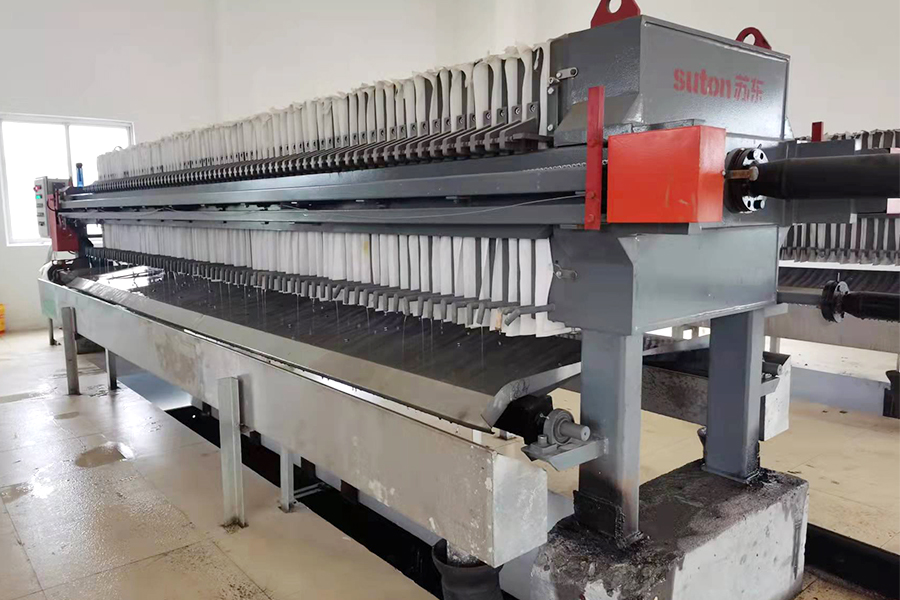
A Filter Press is a batch filtration device that uses hydraulic or mechanical pressure to separate solids from liquids. This type of filtration system is particularly useful when high-efficiency solid-liquid separation is required, and when the separation of fine particles is essential.
The process involves feeding slurry (a mixture of solids and liquids) into the filter press. The slurry is then subjected to pressure that forces the liquid through a series of filter plates, leaving the solids behind as a filter cake. The liquid that passes through the plates is known as the filtrate.
Key Components of a Filter Press:
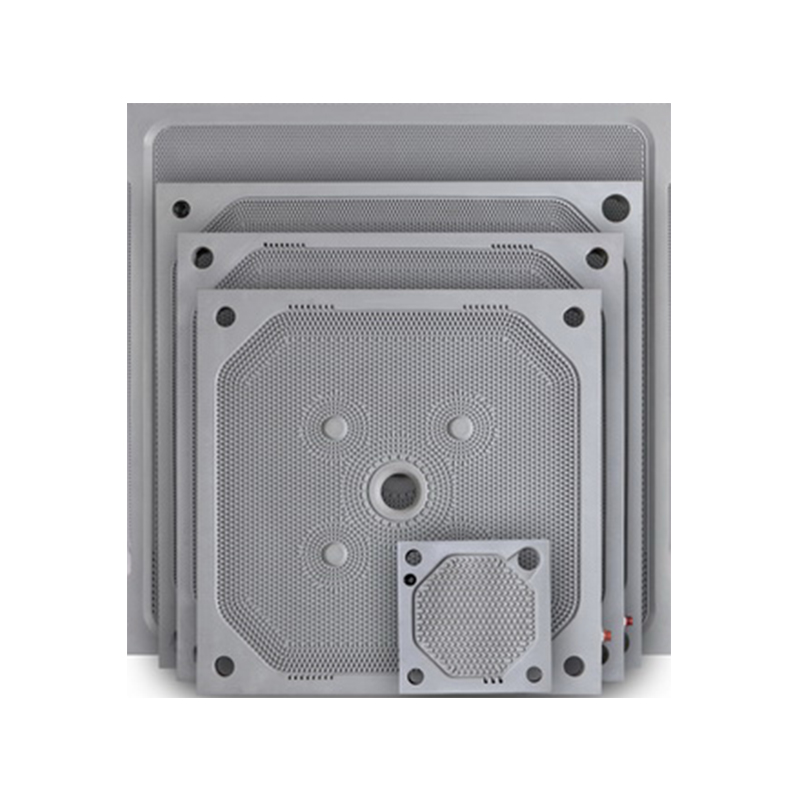
- Filter Plates: These are arranged in a stack and are separated by filter cloths.
- Filter Cloths: Used to filter out the solid particles from the liquid.
- Hydraulic or Mechanical Pressing System: Provides the pressure required for filtration.
- Cake Discharge Mechanism: Used to unload the solids (filter cake) after the filtration process.
How It Works
- Loading: The slurry is pumped into the filter press.
- Filtration: The press uses hydraulic or mechanical force to compress the filter plates, forcing liquid to pass through the filter cloth while the solid particles are trapped.
- Cake Formation: As the filtration process continues, the solids form a thick, compact layer (filter cake) on the plates.
- Unloading: Once the filtration cycle is complete, the filter press is opened, and the filter cake is removed. A new batch can then be loaded into the system.
What Is a Belt Filter?
Definition and Functionality
A Belt Filter is a continuous filtration device designed for large-scale filtration processes. It typically uses a conveyor belt that carries the slurry through a series of filtration zones, where water or liquid is separated from the solid materials. Belt filters rely on gravity and minimal pressure to remove liquid from the slurry.
Key Components of a Belt Filter:
- Conveyor Belt: A continuous, porous belt that moves the slurry through the filtration zones.
- Filtration Zone: The area where liquid is separated from the solids.
- Rollers and Draining System: Used to support and move the belt while facilitating liquid drainage.
- Cake Discharge Area: The location where the filtered solids are removed from the belt.
How It Works
- Feeding: The slurry is continuously fed onto the moving belt.
- Filtration: As the slurry moves through the filtration zone, gravity helps pull the liquid out, and some additional pressure is applied by the belt to aid the separation.
- Dewatering: The water drains through the belt, leaving behind a layer of solid particles (filter cake) on the belt.
- Cake Removal: The filter cake is discharged from the belt as it exits the system, while the filtered liquid is collected for further processing or disposal.
Key Differences Between Filter Press and Belt Filter
Filtration Method
- Filter Press: Utilizes hydraulic or mechanical pressure to achieve high-efficiency filtration. The filtration process is batch-based and produces a drier filter cake with a high degree of separation between solids and liquids.
- Belt Filter: Relies on gravity and minimal pressure for filtration. It works continuously and is typically used for processes that require high volumes of slurry to be filtered over an extended period.
Operation Mode
- Filter Press: Operates in batch mode, which means it completes one filtration cycle at a time. After each cycle, the filter press must be unloaded and reloaded with fresh slurry before starting the next cycle.
- Belt Filter: Operates in a continuous mode, meaning that slurry is fed into the system continuously, and the filtration process never stops. The belt moves continuously to filter large volumes of material.
Filtration Capacity
- Filter Press: Generally suited for medium to small-scale filtration processes. Due to its batch nature, it is more efficient in handling materials that require high filtration pressure and a dry filter cake.
- Belt Filter: Better suited for large-scale operations that require continuous filtration of large quantities of slurry. Its filtration capacity is higher due to its continuous nature.
Cake Quality
- Filter Press: Produces a drier filter cake with a low residual moisture content. This is important when the solids need to be further processed or disposed of in a dry state.
- Belt Filter: Produces a wetter filter cake with a higher moisture content. This can be less desirable in applications where the solids need to be dry.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Filter Press
- Higher Filtration Efficiency: Filter presses provide high pressure, resulting in a better separation of solids and liquids.
- Drier Filter Cake: The pressure helps produce a drier filter cake, which is beneficial in many industries, such as mining, where the solids need to be removed and disposed of with minimal moisture.
- Flexibility: Filter presses can handle a variety of materials, from fine slurries to coarse particles.
- Compact Design: They require less space compared to belt filters, making them suitable for operations with limited floor space.
Disadvantages of Filter Press
- Batch Operation: Since filter presses work in cycles, they are not ideal for continuous processes.
- High Maintenance: Filter presses require regular maintenance and cleaning, particularly the filter cloths and the hydraulic systems.
- Labor-Intensive: The process of unloading the filter cake and cleaning the system can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
Advantages of Belt Filter
- Continuous Operation: Belt filters can operate continuously, making them ideal for high-volume operations.
- Low Maintenance: Belt filters require less maintenance due to their simple mechanical design.
- High Throughput: Ideal for industries that need to filter large quantities of slurry, such as pulp and paper or food processing.
Disadvantages of Belt Filter
- Lower Filtration Efficiency: Since belt filters use gravity and minimal pressure, they may not provide as high filtration efficiency as filter presses.
- Wetter Cake: The filter cake produced is typically wetter, which might not be suitable for all applications.
- Larger Space Requirement: Belt filters are generally larger in size and require more space to accommodate their continuous operation.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Filter Press | Belt Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration Method | Pressure-driven | Gravity and minimal pressure |
| Operation Mode | Batch | Continuous |
| Filtration Efficiency | High, produces drier cakes | Moderate, produces wetter cakes |
| Cake Quality | Drier, lower moisture content | Wetter, higher moisture content |
| Maintenance | High, due to complex mechanisms | Low, simpler mechanical systems |
| Space Requirements | Compact | Larger, requires more space |
| Best for | High-efficiency filtration, small to medium-scale | High-volume continuous filtration |
When Should You Choose a Filter Press?
A Filter Press is ideal for industries and applications that require high filtration efficiency, a dry filter cake, and can accommodate a batch process. It is well-suited for:
- Chemical processing: Where precise separation of solids and liquids is essential.
- Mining: Where dewatering of mined materials requires a dry filter cake.
- Wastewater treatment: For industries that need to treat water and produce dry sludge for disposal.
When Should You Choose a Belt Filter?
A Belt Filter is a better option for large-scale continuous filtration where high throughput is essential. It works well in:
- Pulp and paper industry: For dewatering paper pulp.
- Food and beverage: For continuous filtration of liquids like juices or oils.
- Municipal wastewater treatment: For continuous dewatering of sludge.

 English
English Español
Español हिंदी
हिंदी Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt